why does intermittent fasting burn fat Guide to intermittent fasting
Intermittent fasting is gaining popularity as a health trend, and for good reason. For those who are unfamiliar with the concept, intermittent fasting involves alternating periods of fasting and eating. It is not a diet, but rather an eating pattern. This method has been found to have various health benefits, both physically and mentally.
Pin on Healthy Life
 One of the advantages of intermittent fasting is that it aids in weight loss. When we fast, our body has a chance to burn stored fat for energy. This can lead to a decrease in body fat and a reduction in overall weight. Additionally, intermittent fasting has been found to increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent type 2 diabetes.
One of the advantages of intermittent fasting is that it aids in weight loss. When we fast, our body has a chance to burn stored fat for energy. This can lead to a decrease in body fat and a reduction in overall weight. Additionally, intermittent fasting has been found to increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent type 2 diabetes.
Intermittent fasting has also shown promise in improving cardiovascular health. Studies have suggested that this eating pattern can reduce blood pressure and cholesterol levels. By giving our body a break from constant digestion, it has a chance to repair damaged cells and improve overall heart health.
Additionally, intermittent fasting has been linked to improved brain health. Some research suggests that it may help protect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Fasting promotes the production of a protein called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is responsible for the growth and protection of neurons. This increase in BDNF levels may enhance brain function and slow down age-related cognitive decline.
Intermittent Fasting for Health - Dr. Betsy Rice, ND
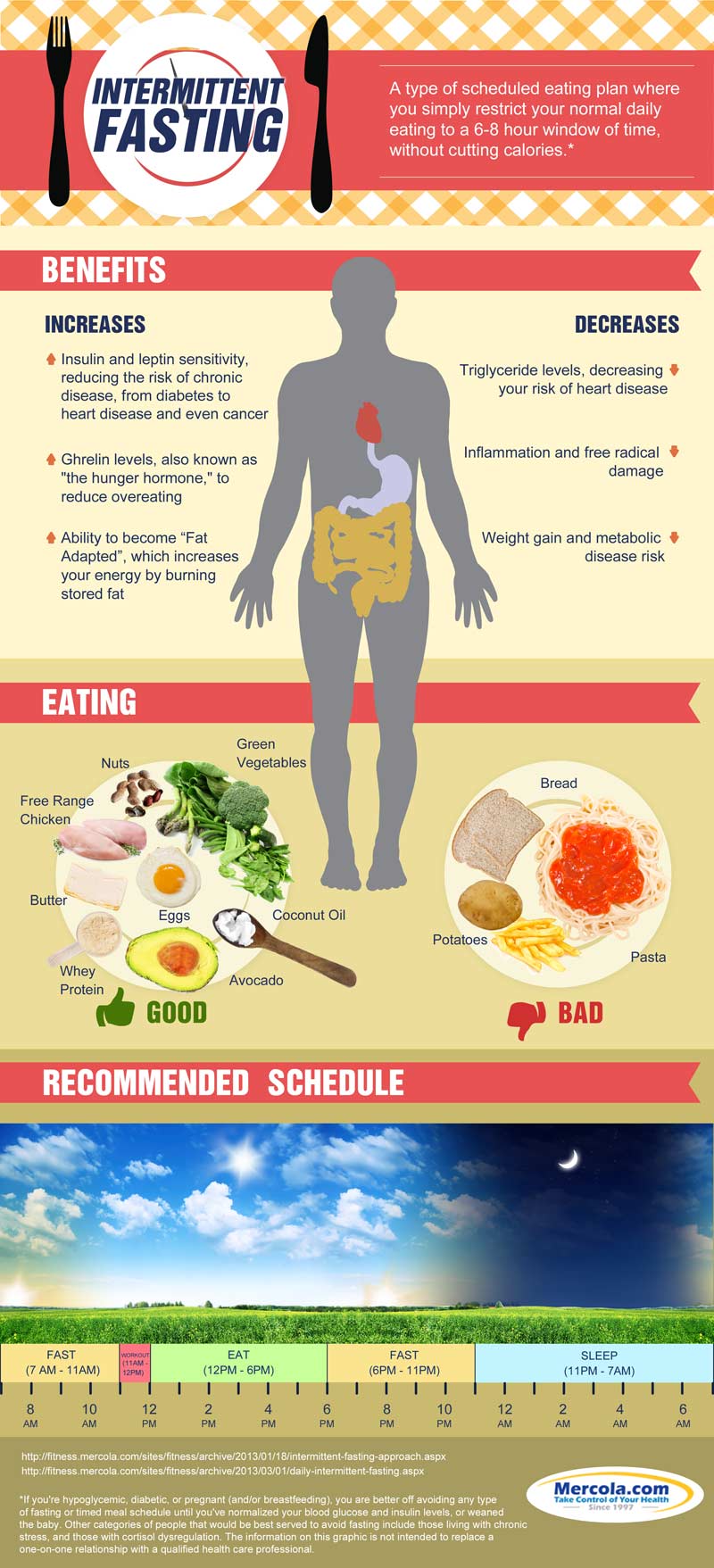 Another benefit of intermittent fasting is its potential anti-aging effects. Fasting triggers a cellular process called autophagy, which involves the breaking down and recycling of old or damaged cells. This can lead to a rejuvenation of our body at a cellular level and potentially slow down the aging process.
Another benefit of intermittent fasting is its potential anti-aging effects. Fasting triggers a cellular process called autophagy, which involves the breaking down and recycling of old or damaged cells. This can lead to a rejuvenation of our body at a cellular level and potentially slow down the aging process.
Intermittent fasting has also been shown to improve our sleep quality. By allowing our digestive system to rest during fasting periods, we can experience deeper and more restful sleep. Adequate sleep is essential for overall well-being and can have a positive impact on mood, cognitive function, and immune health.
While intermittent fasting can offer numerous health benefits, it is important to approach it in a balanced and sustainable manner. It is essential to listen to your body and ensure that you are still receiving an adequate intake of nutrients during your eating periods. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary regimen.
Overall, intermittent fasting is a promising approach to improve health, promote weight loss, and potentially extend our lifespan. By giving our digestive system a break and allowing our body to tap into its fat stores, we can optimize our overall well-being. However, it is crucial to approach fasting with caution and consider individual health needs and preferences.
If you are searching about How to do Intermittent fasting (IF)| Things you MUST know | BURN THAT you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pics about How to do Intermittent fasting (IF)| Things you MUST know | BURN THAT like Pin on Healthy Life, Intermittent Fasting for Health - Dr. Betsy Rice, ND and also Intermittent Fasting for Health - Dr. Betsy Rice, ND. Here it is:
How To Do Intermittent Fasting (IF)| Things You MUST Know | BURN THAT
 www.youtube.comfasting intermittent fat burn
www.youtube.comfasting intermittent fat burn
Intermittent Fasting For Health - Dr. Betsy Rice, ND
 www.drbetsyrice.comfasting intermittent health dr
www.drbetsyrice.comfasting intermittent health dr
Pin On Healthy Life
 www.pinterest.comfasting intermittent hormone
www.pinterest.comfasting intermittent hormone
Guide To Intermittent Fasting - Does Coffee Creamer Break Your Fast?
 thesouthernsource.comfasting intermittent infographic deficit caloric benefits prevention thesouthernsource sott
thesouthernsource.comfasting intermittent infographic deficit caloric benefits prevention thesouthernsource sott
Why Intermittent Fasting Burns Fat Faster And For Good
 www.healthfittness.co.ukfasting ayuno intermittent intermitente bajar consiste aspetti negativamente influiscono psicologici programa
www.healthfittness.co.ukfasting ayuno intermittent intermitente bajar consiste aspetti negativamente influiscono psicologici programa
Fasting intermittent health dr. Guide to intermittent fasting. Fasting intermittent hormone