what happens during the g1 and g2 phases of interphase Interphase microbenotes mitosis mitotic uncontrolled produces nucleus
The cell cycle is a fundamental process that enables cells to grow and divide. It consists of several stages, including interphase and mitosis, followed by cytokinesis. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the accurate replication and distribution of DNA. In this post, we will delve into the details of interphase and its significance in the cell cycle.
Interphase - Stage 1
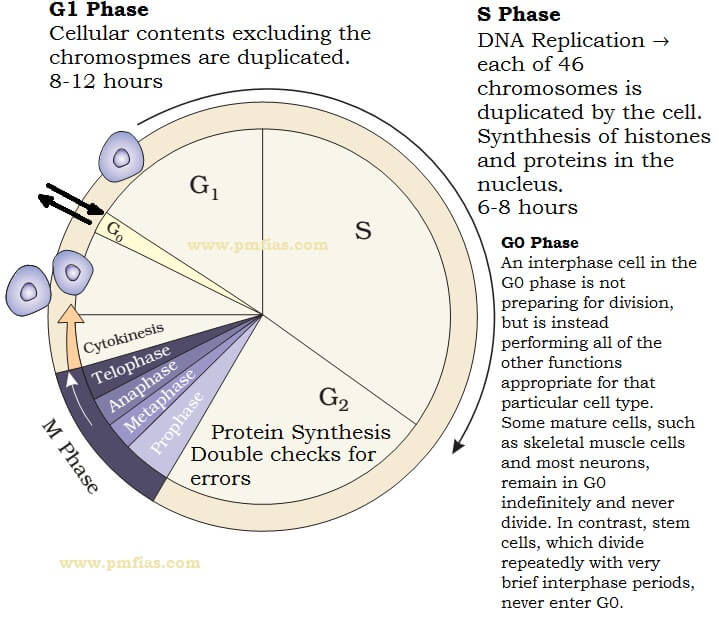
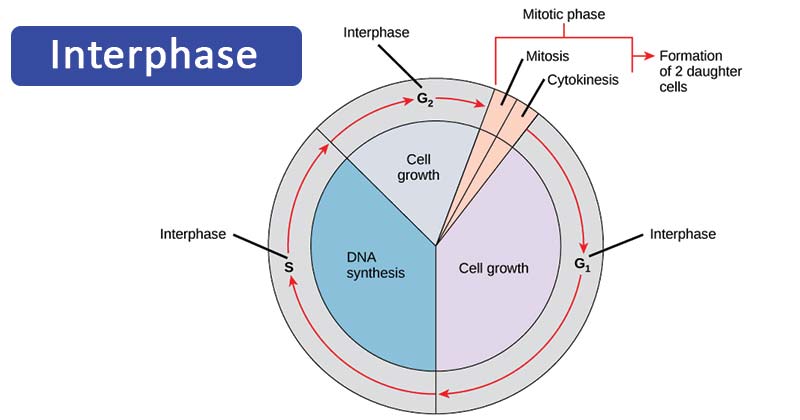
Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle and can be further divided into three sub-stages: G1, S, and G2.
 G1 Phase: During the G1 phase, the cell grows in size and prepares for DNA replication. It is a critical checkpoint for the cell, where it assesses external signals and internal conditions to determine whether to proceed into the next phase.
G1 Phase: During the G1 phase, the cell grows in size and prepares for DNA replication. It is a critical checkpoint for the cell, where it assesses external signals and internal conditions to determine whether to proceed into the next phase.
S Phase: The S phase is the synthesis phase, where DNA replication occurs. The cell duplicates its entire genome, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic information.
G2 Phase: In the G2 phase, the cell continues to grow and prepares for mitosis. It checks for DNA errors and ensures that the replicated chromosomes are intact and ready for cell division.
Mitosis - Stage 2
Mitosis is the process of dividing the cell’s nucleus into two identical nuclei. It is divided into four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase: During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope begins to break down. Centrosomes, which contain the microtubules involved in cell division, migrate to opposite poles of the cell.
Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell during metaphase. Microtubules attach to the centromeres of each chromosome, forming the mitotic spindle apparatus.
Anaphase: Anaphase is characterized by the separation of sister chromatids. The microtubules pull the sister chromatids apart, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an equal set of chromosomes.
Telophase: Telophase marks the final stage of mitosis. The nuclear envelope reforms around the separated sister chromatids, and the chromosomes begin to decondense. The cell starts to divide during cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis - Stage 3
Cytokinesis follows the completion of mitosis and involves the physical division of the cell into two daughter cells. In animal cells, a contractile ring composed of actin and myosin filaments forms around the equator of the cell. The ring contracts, creating a furrow that eventually pinches the cell apart.
In plant cells, a structure called the cell plate forms during cytokinesis. The cell plate is made up of vesicles containing cell wall components. These vesicles fuse together and gradually extend across the equator of the cell, dividing it into two daughter cells, each with its own cell wall.
 Interphase plays a critical role in the cell cycle by allowing the cell to grow, replicate its DNA, and prepare for division. It is during this stage that the cell performs crucial functions such as transcription and translation, which contribute to its overall growth and function.
Interphase plays a critical role in the cell cycle by allowing the cell to grow, replicate its DNA, and prepare for division. It is during this stage that the cell performs crucial functions such as transcription and translation, which contribute to its overall growth and function.
Understanding the intricacies of the cell cycle, including interphase, can provide valuable insights into various developmental processes, tissue regeneration, and the development of diseases such as cancer. Researchers continue to study this essential biological process to unravel its complexities and uncover potential therapeutic targets for various conditions.
Overall, interphase serves as a crucial bridge between cell growth and division, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information to future generations of cells.
If you are looking for Interphase Stage Of The Cell Cycle you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Images about Interphase Stage Of The Cell Cycle like Interphase Stage Of The Cell Cycle, Interphase: Definition, Stages, Cell Cycle, Diagram - PhD Nest and also Interphase - Stage 1 Interphase Stage 2 Mitosis Stage 3 Cytokinesis Ppt. Here you go:
Interphase Stage Of The Cell Cycle
 knowledgetriviasample.blogspot.comInterphase - Stage 1 Interphase Stage 2 Mitosis Stage 3 Cytokinesis Ppt
knowledgetriviasample.blogspot.comInterphase - Stage 1 Interphase Stage 2 Mitosis Stage 3 Cytokinesis Ppt
 arnettet-barn.blogspot.cominterphase cell mitosis cycle division stage progression diagram phase cytokinesis which researchgate figure cloud ppt services
arnettet-barn.blogspot.cominterphase cell mitosis cycle division stage progression diagram phase cytokinesis which researchgate figure cloud ppt services
Pin On Diferencia Entre
 www.pinterest.comMitosis | Cell Cycle | Cell Division | PMF IAS
www.pinterest.comMitosis | Cell Cycle | Cell Division | PMF IAS
 www.pmfias.commitosis cell interphase g1 phases interval dna g2 replication cytokinesis replicate synthesis
www.pmfias.commitosis cell interphase g1 phases interval dna g2 replication cytokinesis replicate synthesis
Interphase: Definition, Stages, Cell Cycle, Diagram - PhD Nest
 www.phdnest.cominterphase microbenotes mitosis mitotic uncontrolled produces nucleus
www.phdnest.cominterphase microbenotes mitosis mitotic uncontrolled produces nucleus
Interphase microbenotes mitosis mitotic uncontrolled produces nucleus. Interphase: definition, stages, cell cycle, diagram. Interphase stage of the cell cycle